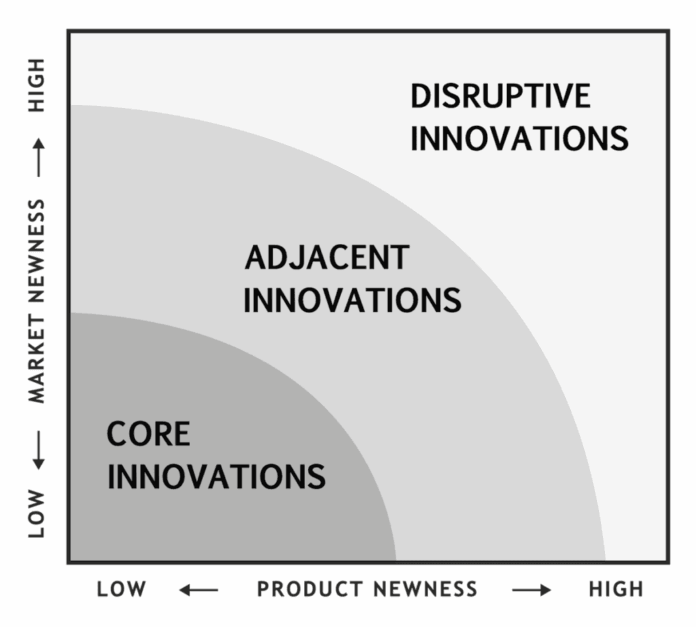
What do incremental enhancements of a legacy app and the event of a brand new AI product have in frequent? Each should create worth and innovate to some extent. On this article, I focus on the Innovation Ambition Matrix, a device that helps you perceive your product’s innovation kind and, primarily based on it, make the best strategic choices and optimise your product portfolio.
Hearken to the audio model of this text:
Overview of the Matrix
The Innovation Ambition Matrix, which was developed by Bansi Nagji and Geoff Tuff, considers the novelty of the product on its horizontal axis and the novelty of the market on the vertical axis. This enables us to tell apart three totally different innovation sorts: core, adjoining, and disruptive, as Determine 1 reveals.[1]
Observe that Nagji and Tuff use the time period transformational as an alternative of disruptive. Some folks additionally discuss with core improvements as incremental and to adjoining ones as evolutionary.[2]
Core Improvements
Core improvements optimise present merchandise for established markets. They draw on the abilities and belongings your organization already has in place, and so they make incremental adjustments to present merchandise. These initiatives are actually core to what you are promoting, as they generate at this time’s revenues. Most of your organization’s merchandise are prone to be on this class—except you’re employed for a start-up. Examples of core improvements embrace Microsoft Home windows and Microsoft 365, previously referred to as Workplace. Each are main income sources for the corporate. The longer-term progress potential of core merchandise, nonetheless, is low, and so is the quantity of threat and uncertainty current. Should you consider the product life cycle and its levels, then core improvements sometimes correspond to mature merchandise.
Adjoining Improvements
Adjoining improvements take one thing your organization does nicely into a brand new area—for example, providing an present product in a market that’s new to the corporate or creating a brand new product for a market you already serve. Take, for instance, the Apple Watch and the Google Chrome browser. In each instances, the businesses entered present markets—wearables and net browsers, respectively—with a brand new product.
Disruptive Improvements
Adjoining improvements give you the advantage of leveraging present belongings. This makes the problem of innovating efficiently extra manageable, no less than to a sure extent. Sadly, additionally they have a major drawback. They handle an present market, and their progress prospects are restricted by your means to develop the market and seize extra market share—that’s, to draw extra customers and clients.
To expertise larger long-term progress, your organization has to spend money on disruptive improvements. Apple, for example, disrupted the cell phone market with the unique iPhone; Nintendo did the identical within the video games console market with its Wii; and Amazon disrupted the retail guide market with its on-line retailer.[3]
The Innovation Ambition Matrix and Product Technique
As soon as you recognize your product’s innovation kind, you should utilize it to grasp the technique work required and make the best strategic choices.
Core Improvements
As they’re essential to producing the required earnings, it’s best to defend your core merchandise. Concentrate on incrementally enhancing options, fixing bugs, and optimising the prevailing enterprise mannequin. For the reason that quantity of uncertainty is low, the strategizing effort is relatively small. You must due to this fact deal with steady strategizing: Spend a number of hours per week to overview the product efficiency utilizing the acceptable KPIs, perform competitor analysis, uncover related developments, and maintain quarterly technique workshops to have a look at larger improvement and modify the product technique.
Adjoining Improvements
Issues are totally different in relation to adjoining merchandise. To succeed with them, you’ll have to hold out product technique discovery, analysis the market, develop a radical understanding of the consumer and buyer wants, in addition to the aggressive panorama and related developments. Moreover, you could have to analyze new applied sciences and overview whether or not the present enterprise mannequin must be tailored.
You have to due to this fact be capable to take knowledgeable dangers and really feel secure to experiment and make errors. As the quantity of threat and uncertainty current is significantly larger than in core improvements, you require extra time to find an efficient product technique, usually a number of weeks to a few months.
Disruptive Improvements
As vital as disruptive merchandise are for enabling future progress and securing the long-term prosperity of what you are promoting, most established firms wrestle to leverage them successfully. Right here is why: To realize disruption, an organization should do issues in a different way and disrupt itself, no less than to a sure extent. It has to discontinue a number of the practices which have helped it turn into profitable, purchase new expertise, discover new enterprise fashions, and sometimes embrace, and in some instances develop, new applied sciences.[4]
Consider the contact display for the iPhone and the movement controller for the Wii, for instance.[5] The trouble to create an efficient product technique is due to this fact even larger than for adjoining improvements. It could take you many months to discover a technique that’s prone to end in a useful, technically possible, economically viable, and moral product.
What’s extra, succeeding with disruptive improvements requires an entrepreneurial mindset. You’ll have to have the ability to experiment with new processes, applied sciences, and instruments, make errors, fail, and get better shortly. Utilizing an incubator may help you with this. An incubator is a brand new, momentary enterprise unit that’s loosely coupled to the remainder of the organisation. It presents the autonomy to do issues in a different way and develop brand-new merchandise. As Peter Drucker writes in his guide Innovation and Entrepreneurship, “The most effective, and maybe the one, method to keep away from killing off the brand new (…) is to arrange the modern challenge from the beginning as a separate enterprise.”[6]
Determine 2 summarises the strategizing effort for the three innovation sorts.
The Innovation Ambition Matrix and Portfolio Administration
Up to now, I’ve centered on the connection between the innovation kind and the product technique. However that’s not all of the Innovation Ambition Matrix can be utilized for. The truth is, it was created to assist firms successfully handle their product portfolios.
As a rule of thumb, established firms ought to focus about 70% of their innovation efforts on core improvements, roughly 20% on adjoining ones, and about 10% on disruptive improvements, based on Nagji and Tuff. This helps firms create a balanced portfolio that generates the required earnings (core merchandise) and invests in future income sources (adjoining and disruptive merchandise).
Over time, profitable disruptive and adjoining merchandise flip into core ones. instance is the iPhone. Whereas the primary model was a disruptive innovation, it has turn into a significant income supply for Apple. The underside line is: To develop organically, firms should regularly search for new progress alternatives and spend money on adjoining and disruptive merchandise—the merchandise that generate tomorrow’s money.[7]
Because the 70-20-10 rule is a basic suggestion, chances are you’ll nicely have to regulate the odds in your firm. For instance, a know-how agency might spend solely 45% of its innovation effort on core improvements, however 40% on adjoining and 15% on disruptive ones. Examine this to a longtime shopper firm, which can profit from investing as much as 80% in core improvements.[8] It doesn’t matter what ratio is best for you, just be sure you often overview the product portfolio and spend money on new innovation initiatives.
Notes
[1] Bansi Nagji and Geoff Tuff, “Managing Your Innovation Portfolio,” Harvard Enterprise Assessment, Might 2012.
[2] The Innovation Ambition Matrix relies on the Ansoff matrix, which explores the connection between the product and the market. It distinguishes an present product from a brand new product and an present market from a brand new one. This offers rise to 4 progress methods: market penetration, product improvement, market improvement, and diversification. Market penetration means incrementally enhancing an present product to extend its market share. Product improvement entails creating a brand new product for an present market—a market you already serve. Market improvement refers to coming into a market that’s new to your organization with an present product. Diversification implies creating a brand new product for a brand new market. See Igor Ansoff, “Methods for Diversification,” Harvard Enterprise Assessment 35, Sep–Oct 1957.
[3] A disruptive innovation sometimes solves a buyer downside in a greater, extra handy, or cheaper method than present options (see Clayton Christensen’s guide The Innovator’s Dilemma, which I’ve referenced in footnote 4). It leads to not solely a brand new product, nevertheless it additionally creates a brand new market by addressing nonconsumption: It attracts individuals who didn’t reap the benefits of related merchandise. However because the disruptive product matures, it makes inroads into a longtime market, reconstructs market boundaries, and disrupts the market. Take the iPhone for example. The established gamers, together with Nokia and BlackBerry, didn’t understand the unique iPhone as a risk; its enterprise options, similar to electronic mail integration, had been too weak. However because the iPhone improved and provided an growing vary of enterprise and productiveness apps, an increasing number of folks started to make use of the product, the market share of Nokia and BlackBerry telephones began to say no, and the excellence between enterprise and shopper segments turned irrelevant.
[4] See Clayton Christensen, 1997, The Innovator’s Dilemma, Harvard Enterprise College Press, and Clayton Christensen and Michael Raynor, 2013, The Innovator’s Answer, 2nd ed., Harvard Enterprise Assessment Press.
[5] Observe {that a} disruptive know-how like generative AI doesn’t routinely obtain disruption. As defined in footnote 3, a disruptive innovation creates a brand new market along with a brand new product.
[6] Peter Drucker, 1985, Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Harper & Row, p. 163.
[7] That is consistent with suggestions of different portfolio administration instruments just like the Product Portfolio Matrix, which I focus on within the aptly named article The Product Portfolio Matrix.
[8] See Bansi Nagji and Geoff Tuff, “Managing Your Innovation Portfolio,” Harvard Enterprise Assessment, Might 2012, p. 71.